Secure digital communications have always been a requirement for mission-critical applications and business transactions and communications. That trust hinges on verifying the identity of the individuals and the systems that provided the credentials for that user, system, or device like in internet of things (iOT) use cases.
Let’s take a look at how PKI helps verify identities in secure communications, what some of the essential PKI components are as well as some of the complexities involved, and how you can simplify the management of digital certificates with Axway.
A (very) brief history of internet security and the birth of PKI
Remember how sending and receiving data through the Internet started with just http?
Then, when everybody realized that everything can easily be intercepted and used for malicious causes with http, they required all web sites be https so that at least everything wasn’t clear-text and had some encryption.
Identifying the Web Server side is also important so that users know they are going to the right site and not a malicious fake site looking to trick people into giving up their information.
The only cost-effective and secure way to be able to use the Internet for these mission-critical applications and business flows is to implement an enterprise Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
What is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)?
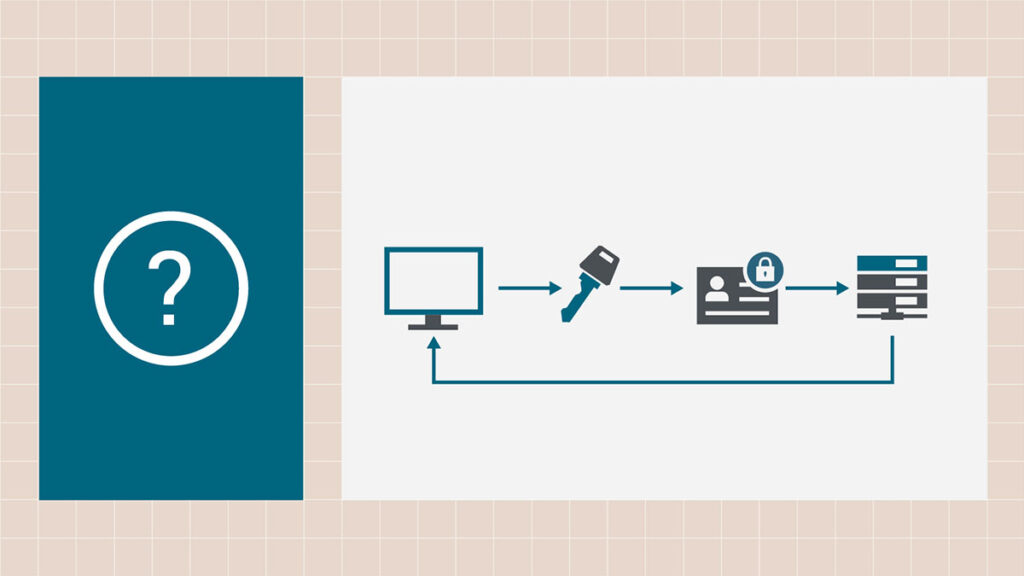
Public Key Infrastructure, or PKI, is a framework for managing data encryption and decryption keys. Each cryptographic key connects to a digital certificate, which verifies the identity of entities in secure communications.
This ensures information remains confidential between senders and recipients. This can also ensure that data has not been tampered with, thanks to non-repudiation digital certificates.
PKI helped solve the costly days of direct connection using expensive phone lines that couldn’t keep up with technological improvements.
PKI validates that users have been vetted – much like when you get your driver’s license. In that case, a person must typically show up in person and get verified by showing proper identification.
They need a passport, birth certificate with raised seal only, perhaps other requirements… A good example in government is what clearance level a user can have – Secret, Top Secret, or Sensitive Compartmented Information (SCI).
You can deploy an enterprise PKI to manage these users and their access to systems, thanks to a user’s PKI certificate containing attributes that describe their roles and access levels.
The other key to securely and properly deploying PKI is to store keys on smart cards – much like your bank card.
It isn’t possible to export the private key off the smart card, so it is a protected and secure way of doing business.
Breaking down essential PKI components
Within a public key infrastructure, several tools and technologies support secure communications.
At PKI’s core, you have public and private keys. Openly shared, the public key encrypts and authenticates a sender’s message. The message can only be decrypted and read by the holder of the private key, which is kept secret.
Digital certificates link a public key to a private key holder’s identity. Issued by a Certificate Authority (CA), these certificates function like a driver’s license or passport, ensuring parties involved in the communication are who they claim to be.
The CA can also act as the Registration Authority (RA). The RA verifies the certificate requester’s credentials and identity before the CA issues a digital certificate.
When a certificate has been revoked or is no longer valid, it’s added to the Certificate Revocation List (CRL). Maintained by the CA, the CRL ensures that no compromised or outdated certificates are trusted or used.
How PKI fits into the modern digital infrastructure
Public key infrastructure is a trust service in today’s increasingly digital world. It assures organizations that their online communications and transactions are secure when the stakes around data breaches are at an all-time high.
As IBM reports, the average cost of a data breach in 2024 was a whopping $4.88 million. That’s a 10% increase from 2023.
Amid these growing security concerns, PKI applications have started to extend beyond the Department of Defense (DoD) and federal government. Industries ranging from financial services to healthcare have taken an interest in using PKI to safeguard sensitive information and preserve trust in digital communications.
That said, most PKI use cases continue to come from the DoD and the federal government. One hang-up: deploying and managing a PKI is complex.
What makes PKI deployment and management complex
As we’ve discussed, digital certificates play a critical role in the PKI infrastructure. Issuing and managing these certificates is one of the more complex aspects of PKI.
At the outset, IT teams must ensure the Certificate Authority is properly linked to cryptographic keys. While critical for establishing trust, this process involves strict checks and balances that can consume IT resources.
See also: Deploying an OCSP architecture with high availability
Once the certificates are established, it becomes a matter of maintaining them. Part of this includes keeping track of certificates’ expiration dates.
If an organization fails to renew certificates before they expire, users encounter security warnings. These messages erode trust or have their access blocked.
In one report, 81% of organizations said they experienced at least two outages due to expired certificates in the past two years. The lack of valid certificates can also hinder the security of encrypted communications and lead to compliance issues when an audit is conducted.
If a PKI certificate is compromised, IT teams must quickly notify the Certificate Authority to revoke it and issue a new one. Any delays in this process can increase the risk of network vulnerabilities.
When issuing the new certificate, IT teams need to ensure that the certificates are properly propagated and integrated to prevent security gaps.
Simplifying the management of digital certificates
Axway Validation Authority (VA) allows for the real-time validation of digital certificates. For organizations with a large certificate footprint, this virtually out-of-the-box-ready solution offers a more robust and scalable option.
With Axway VA, IT teams can look up digital certificates in less time. And the faster IT personnel can look up certificates, the less room there is for latency issues.